By Sina McCullough – Epoch Times
Gardeners can buy a new seed, a genetically modified tomato the FDA barely looked at and GMO proponents hope will win Americans over to more modified foods.
As spring gardening approaches, a new contender has entered the fray—the genetically modified (GM) Purple Tomato. Unlike its GM predecessors, the GM Purple Tomato is not destined solely for the fields of commercial agriculture—it has made its debut in the backyards of home gardeners across the United States.
Development
The GM Purple Tomato was engineered by scientists at Norfolk Plant Sciences in the UK. Led by biochemist Cathie Martin and her team, the project aimed to harness the natural properties of anthocyanins, compounds found in blueberries and blackberries, to enhance the nutritional profile of tomatoes.
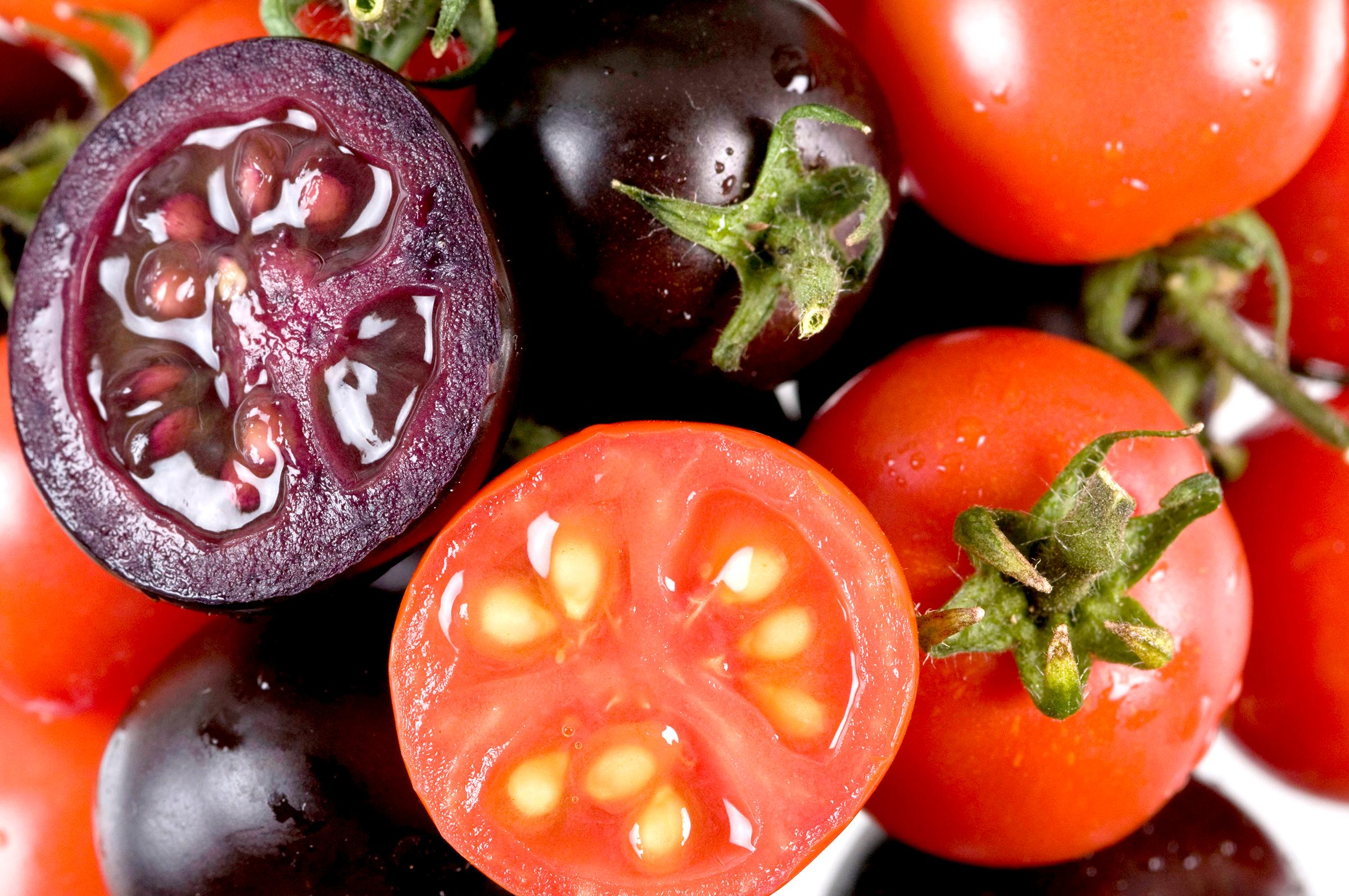

Using genetic engineering techniques, Martin and her colleagues inserted two genes responsible for purple coloration in edible snapdragon flowers into tomato plants. This process enabled the tomatoes to express the genes from the snapdragon and, subsequently, produce high levels of anthocyanins, thereby imbuing the tomatoes with a distinct purple hue and potentially enhanced health benefits.
The genesis of the GM Purple Tomato marks a significant milestone in agricultural biotechnology. Unlike previous GM crops primarily targeted at commercial producers, this tomato is the first GM food crop directly marketed to home gardeners in the United States, offering an opportunity for individuals to engage with biotechnology in their own backyard.

Regulatory Approval
The GM Purple Tomato was deregulated by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) in 2022. According to a statement from the USDA, the GM Purple Tomato is not subject to regulation by the USDA because it does not pose a plant pest risk:“With respect to Norfolk Plant Sciences’ purple tomato, we did not identify any plausible pathways to increased plant pest risk compared to other cultivated tomatoes and issued a response letter indicating the plant is not subject to regulation.”
In 2023, the Purple Tomato received a “no questions” letter from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which means the Purple Tomato is considered “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) and, therefore, does not require premarket review or approval by the FDA.
To qualify for GRAS status, Norfolk Plant Sciences submitted data from tests conducted internally.

Safety Concerns and Health Claims
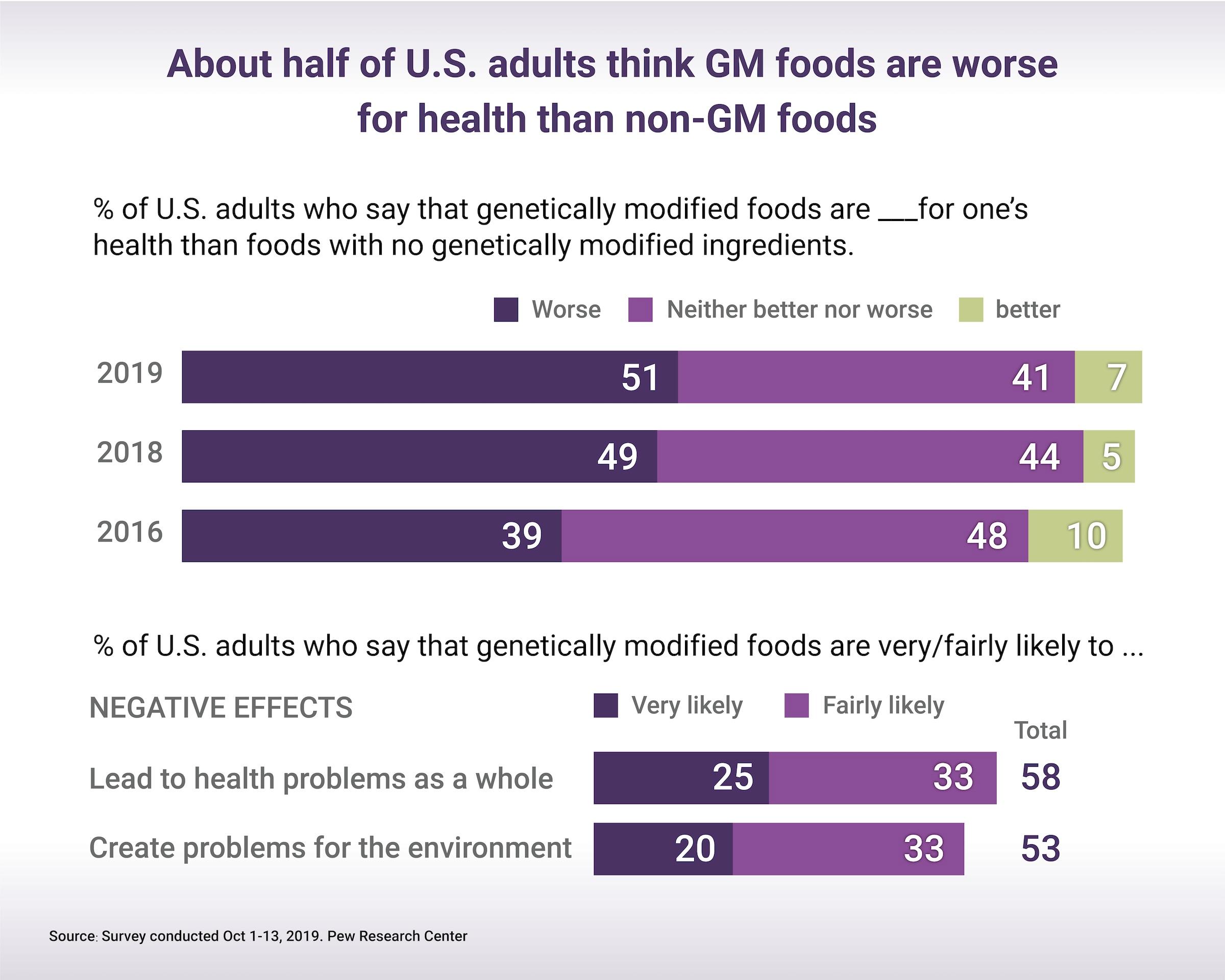
Data provided to the FDA by Norfolk Plant Sciences demonstrates the company conducted various safety tests. However, critics argue the tests are insufficient to guarantee the safety of the Purple Tomato for human consumption.
- The company (Norfolk Plant Sciences) stated that insertion of the foreign DNA was confirmed.
2. PCR and sequence comparison of DNA samples were conducted to confirm the stability of the inheritability of the insertion across generations. Plants were bred to determine if the purple phenotype was inherited in a Mendelian segregation fashion.
- The company stated the purple phenotype was inheritable.
3. Compositional analysis was conducted to determine if the Purple Tomato contained similar nutrients at similar levels compared with non-GMO tomatoes, including protein, fat, carbohydrate, fiber, minerals, carotenoids, vitamins, and alpha-tomatine.
- The company determined the levels of most of the nutritional components to be similar or with “minor differences.”
- The company concluded the level of dietary exposure to anthocyanins is the same as consuming high-anthocyanin foods. For example, 8 ounces of Purple Tomato juice is equivalent to consuming 1 cup of blueberries.
The Controversial Tests
1. Bioinformatic analyses were utilized to determine if any open reading frames were generated or disrupted by inserting the foreign DNA. Norfolk Plant Sciences searched the DNA sequences flanking the insertion sequence in the tomatoes.
- The company reported no open reading frames flanking the insertion location.
Since Norfolk Plant Sciences did not assess possible damage to the entire genome using advanced laboratory techniques, geneticist Michael Antoniou expressed concern in a statement published by GM Watch.
“There’s no evidence that the developers of the GM purple tomato have carried out the kind of molecular analyses (proteomics and metabolomics) that could help establish whether they only got the change they want, with no unintended changes. As a result, we don’t know if these tomatoes are safe to eat,” said Mr. Antoniou.
“We must also bear in mind that the GM transformation process (plant tissue culture and plant cells transformation) will inevitably give rise to hundreds if not thousands of sites of unintended DNA damage (mutations). These wide scale mutations can change patterns of gene function and alter biochemistry and composition, with unknown downstream health consequences,” he said.
- The company identified one “putative” peptide, however, they stated, “this peptide has no homology to any known allergen or protein and there was no evidence this sequence is transcribed in tomato.” They concluded the results “do not raise food safety concerns.”
Allergenicity is an ongoing concern regarding the genetic modification of food. For example, a study published in Nature in 1999 reported that bean plants were genetically modified to produce higher levels of methionine and cysteine but were discarded because the expressed protein of the transgene was highly allergenic.
The Test That Everyone Talked About
Although not included in the 2023 FDA memo, Norfolk Plant Sciences, in conjunction with Cathie Martin, published a pilot feeding study in 2008 in Nature Biotechnology that examined the effects of Purple Tomato supplementation on the life span of cancer-susceptible mice.
According to the study, mice fed the GM tomato lived longer—by an average of 40 days than those fed non-GM red tomatoes.
Publication of the pilot study prompted the John Innes Centre to publish a press release titled, “Purple tomatoes may keep cancer at bay.” (Norfolk Plant Sciences is a spinoff company from the John Innes Centre.)
The UK’s National Health Services (NHS) stated the health claims are not based on benefits documented in humans, but instead are from “a small-scale study of mice,” according to an article published in NHS Choices.
Excessive consumption of anthocyanin may pose an unexpected harm. While it is commonly believed that antioxidants are beneficial and more is preferable, Cancer Research UK suggests this assumption lacks scientific support.“There’s a fair amount of evidence that some antioxidants in our foods can help prevent some kinds of cancer in some people. But the complexity of this evidence often gets translated in the media and in advertising to ‘antioxidants prevent disease’. And that’s not what the science says.”
The Antioxidant Paradox
While anthocyanins have been linked to potential health benefits due to their antioxidant properties, the notion of “more is better” fails to account for the delicate balance within the human body.
Anthocyanins may follow the same pattern of “some is good but too much can be bad.”
Antioxidant supplementation can also increase risk of cancer, according to a 2023 review in the scientific journal Antioxidants.
Antioxidants work, in part, by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals. These ROS are produced naturally during oxygen-based respiration in all living organisms.
It is essential to strike a balance—producing enough ROS to regulate vital functions in the body without generating excessive amounts that lead to damage or disease.
Consequently, Mr. Seidler has raised concern over the quantity of anthocyanins Americans might consume if the GM Purple Tomato replaces its conventional counterpart.
A Solution: Traditionally Bred Alternatives
Traditional plant breeding techniques have already produced a variety of purple tomatoes boasting elevated levels of anthocyanins, without resorting to genetic modification.
Growers already have access to a diverse array of heirloom purple tomato varieties, including the esteemed Black Zebra and Black Beauty.
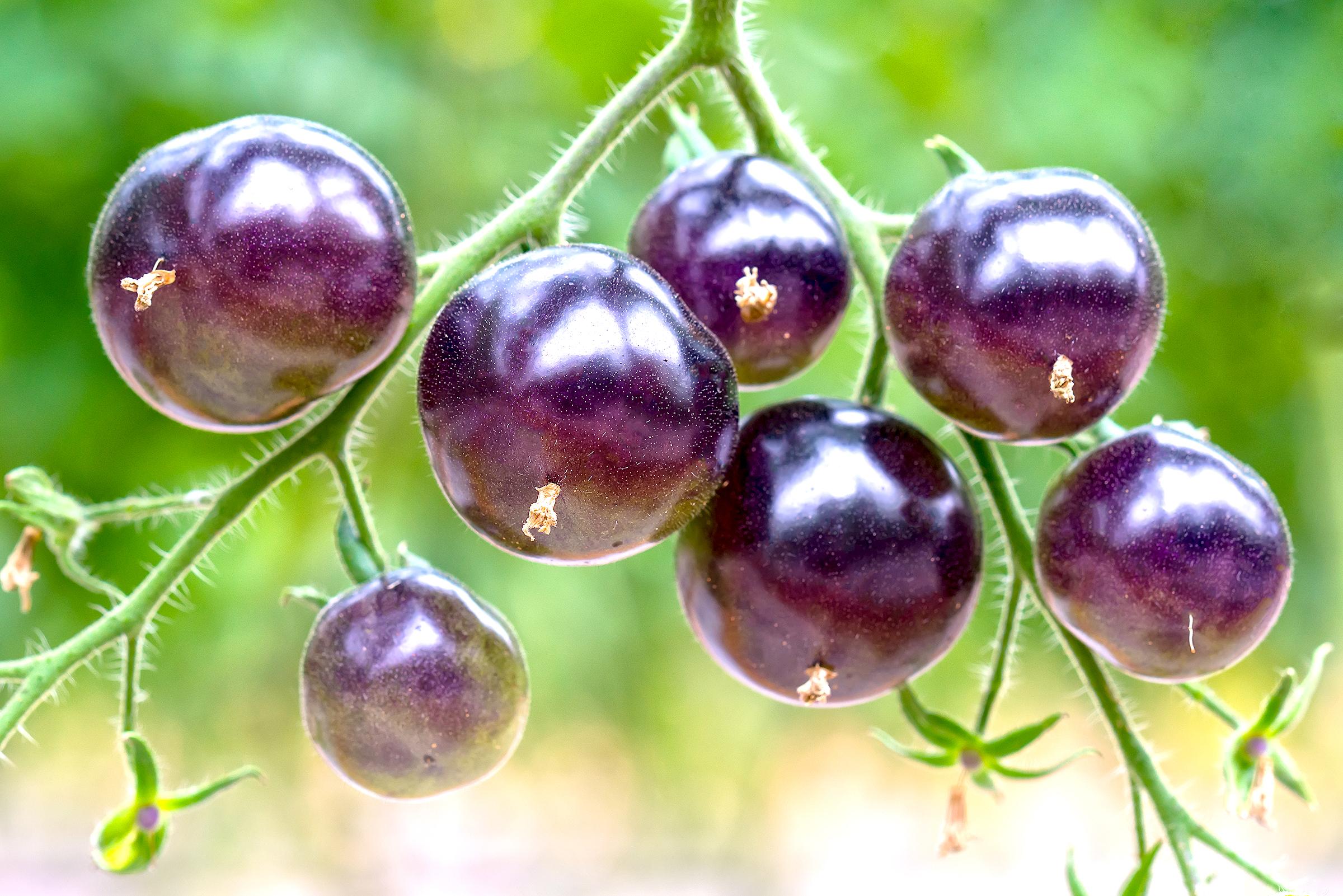

Unlike their domesticated counterparts, which typically harbor anthocyanins in their plant structures and sometimes skin, wild tomatoes employed in the breeding program exhibit these beneficial compounds within their fruits, as highlighted by Mr. Myers. Year after year, Mr. Myers and his team crossed genes, often by hand, from wild tomatoes with modern varieties, until higher levels of anthocyanins could be found in the fruit.
Over two decades since the inception of this breeding program, the “Indigo” cultivars have proliferated to over 50 variants worldwide, finding homes in both small-scale farms and corporate agricultural enterprises.
Broader Implications
The first waves of GM crops were predominantly marketed with the goal of helping farmers feed the world. Food security was at the forefront as crops were engineered to increase yields, resist herbicides, and become more resistant to environmental stressors, such as insect damage and disease.
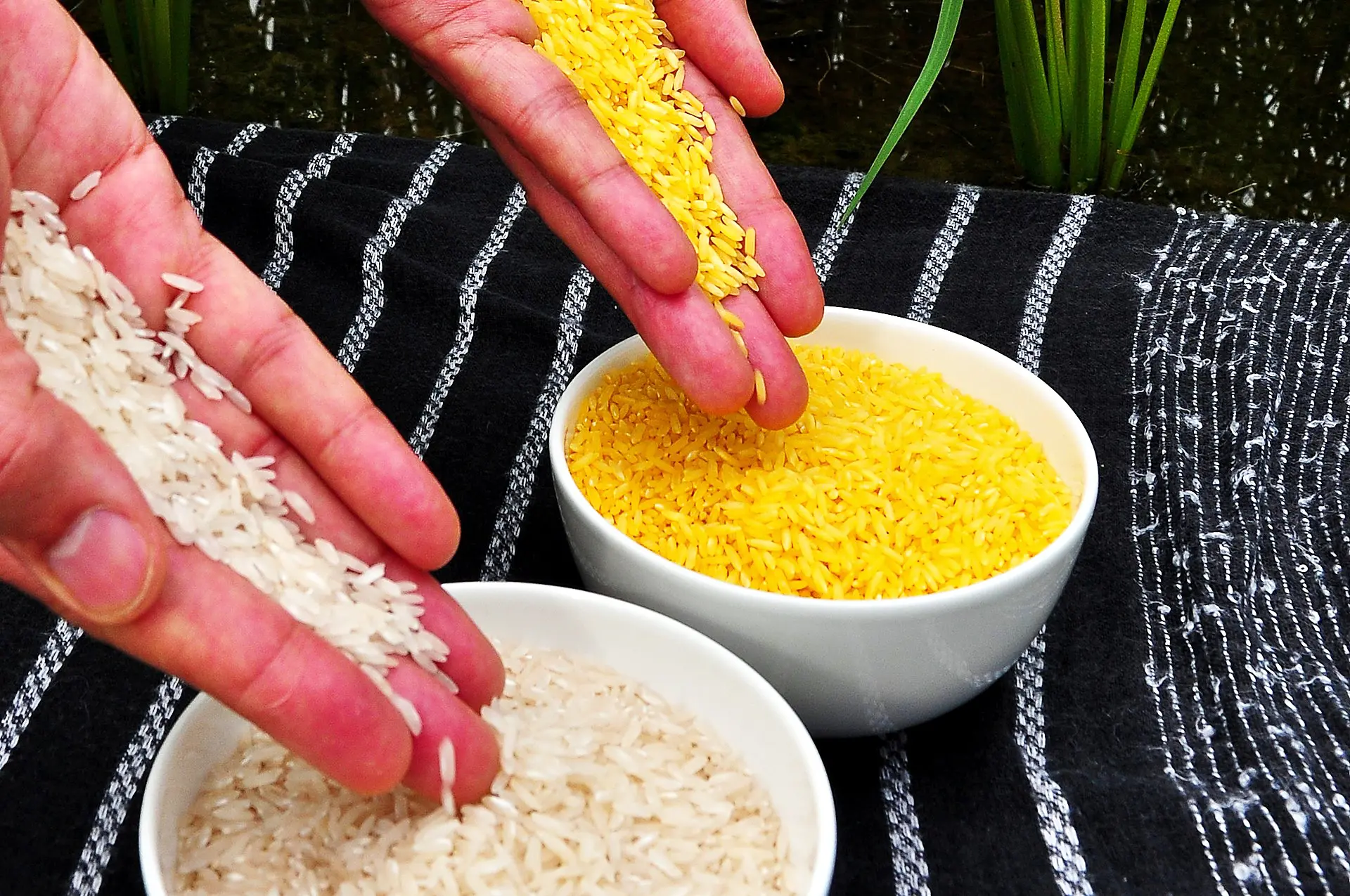
Historically, most crops have not been genetically engineered to increase nutrient density, but rather to better withstand herbicides and pests. One of the few exceptions was golden rice, engineered in the 1990s to contain higher levels of beta-carotene to combat vitamin A deficiency. That crop never gained traction.
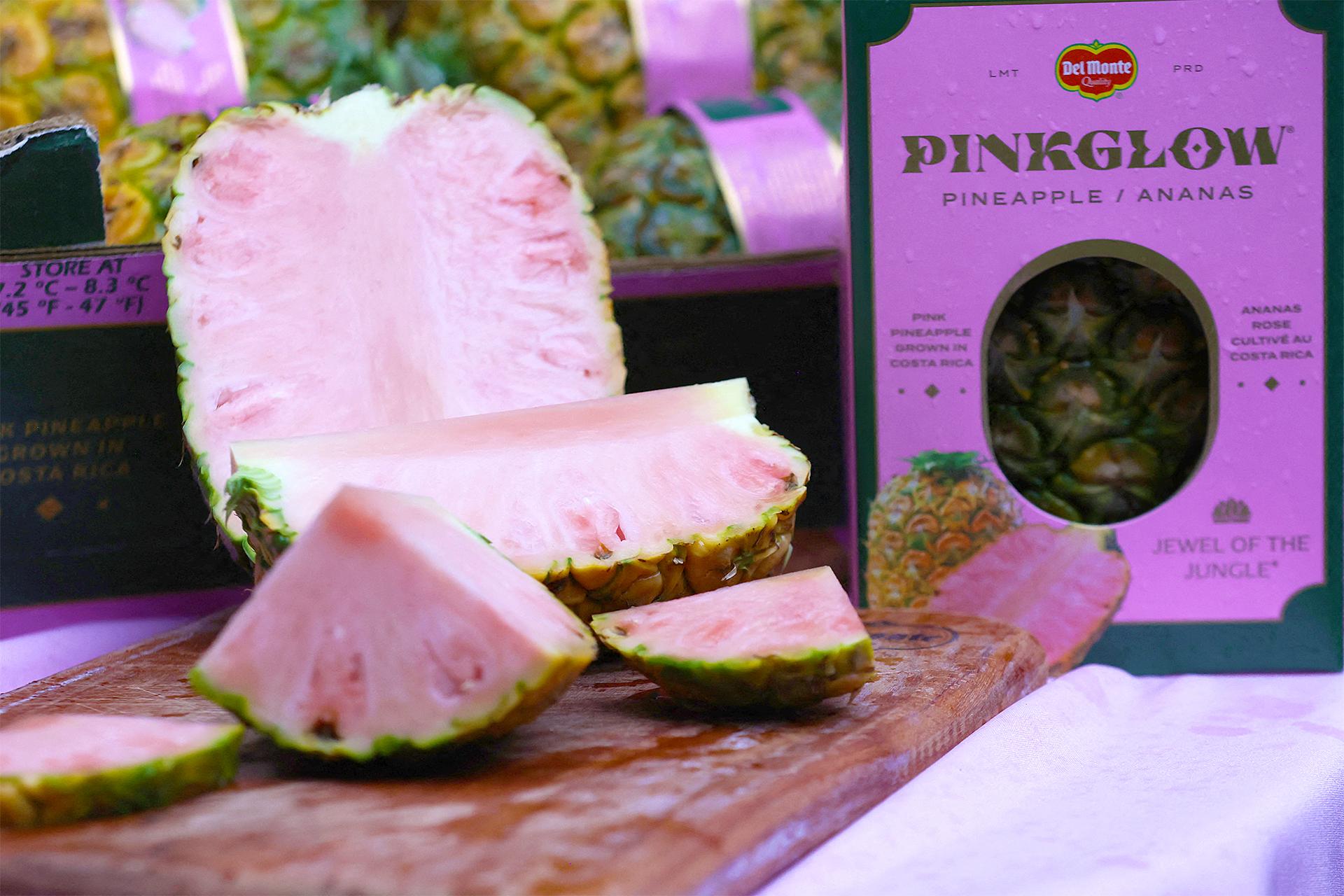


Pink pineapple was created in 2020 by Fresh Del Monte, a California-based company. The rosy flesh contains high levels of lycopene—an antioxidant that gives peaches, tomatoes, and watermelon their rosy hues. However, only Fresh Del Monte is allowed to grow the pink pineapple whereas the Purple Tomato can be grown by farmers or consumers in the United States.
Unlike most of its GM predecessors, the Purple Tomato is marketed as a nutrient-dense food designed to improve health. Why are we witnessing a marketing shift away from food security toward individual health?
Nathan added, “Then it [the GM Purple Tomato] chips away at this negative perception of GMOs and that will enable other products to get out to market that deliver really solid benefits.”
Could the Purple Tomato be a Trojan horse, boasting claims of improved health for the individual while trickling GM seeds into gardens to gain acceptance of GMOs among consumers? Only time will tell.
In a statement to Epoch Times, Joel Salatin, regenerative farmer and co-owner of Polyface Farm, expressed concern about seed drift and patent infringement:“One of the biggest concerns for gardeners is adulteration due to pollen drift. Seed companies often advise up to a mile of distance between varieties to maintain cultivar purity. If you are in an urban or suburban setting, and especially if you do not know all your neighbors or their activities, this kind of distance would be virtually impossible to guarantee. Suddenly you have a being in your garden that you don’t want. And the way courts have ruled, if the cultivar patent owner finds one of your tomatoes with adulterated DNA, you can be liable for patent infringement. What a mess.”
Cathie Martin and her colleague Jonathan Jones from Norfolk Healthy Produce hold active and pending patents on methods to genetically engineer plants with higher antioxidant compounds, as well as the plants made using those methods.
Conclusion
The unveiling of the GM Purple Tomato represents a watershed moment in agricultural biotechnology as the first GM seed marketed to gardeners. Yet, amid the fervor and excitement, we must not lose sight of the complexities and uncertainties that accompany such innovation. Questions remain regarding its safety, efficacy, and long-term implications for human health and the environment.
As scientists, policymakers, and consumers navigate the complex terrain of GMOs, transparency, evidence-based decision-making, and public engagement are essential to fostering informed dialogue as we shape the future of agriculture and our food supply.